We’ve all heard that a high-protein, low-carb diet can help you lose weight—but are they really good for you? Although your body undoubtedly needs protein to function, it is possible to have too much protein.
Protein is an essential nutrient made up of chemical compounds known as amino acids. Your body needs dietary protein to carry out basic functions, especially building and maintaining every cell in the body, including muscles, bones and tissues.
Eating plenty of whole foods that combine lean sources of protein and carbohydrates, healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, minerals and plenty of water is considered optimal for good health. Balance—rather than relying too much on any one nutrient like protein—is key, doctors say.
“It’s important to adjust your protein intake to fit your lifestyle and other nutrient needs, to make sure your body is getting what it needs without overdoing it,” says . Chris MohrPhD, RD, fitness and nutrition consultant at Fortune Recommends Health.
Wondering how much is too much, and what problems it can cause? Keep reading to learn six signs that you’re eating too much protein.
RELATED: 7 Signs of a Protein Deficiency, According to Doctors


The amount of protein you need depends on your age, sex, weight and activity level, to explain Raj DasguptaMD, NCOA medical examiner and ABIM quadruple board certified physician specializing in internal medicine, pulmonology, critical care and sleep medicine.
“In general, adults need about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Athletes and very active people may need more, around 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram. Older people and those recovering from illness may also need more protein to stay healthy,” he says. The Best of Life.
Not sure how to calculate your weight in kilograms? Simply divide your weight in pounds by 2.2.
Getting too little protein can also cause symptoms, Dasgupta notes. He says: “In the short term, you may feel tired, have muscle weakness, and/or have a weakened immune system. “Over time, the lack of protein chronic can cause muscle wasting, impaired growth and development in children, and edema (water retention).”
Mohr adds that it is very important for older people to eat enough protein to maintain muscle strength, prevent infections and promote overall health.
That said, when your diet includes more than two grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, you may start to experience symptoms. These may include the following.
RELATED: 6 Signs You’re Getting Too Much Calcium, According to Doctors
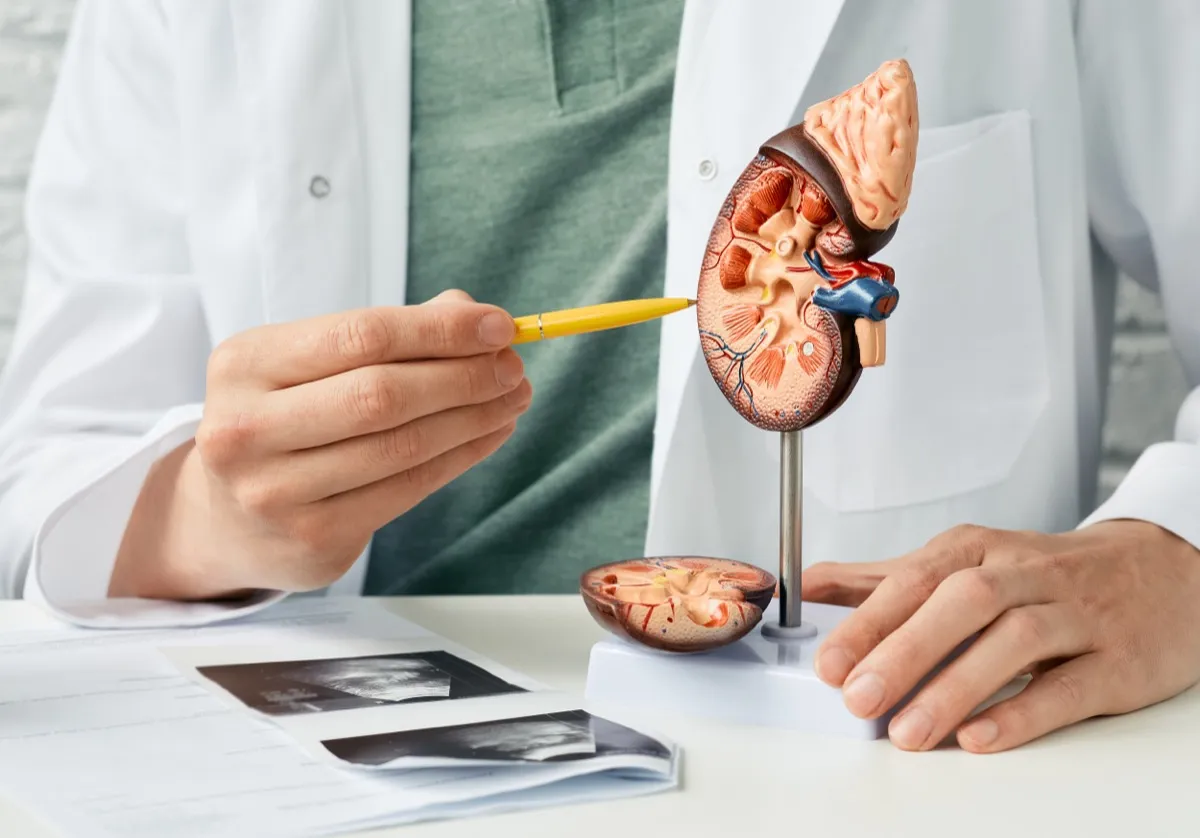

According to Dasgupta, if you already have kidney disease, following a high-protein diet can worsen your kidney function because the body may not be able to remove all impurities associated with proteins.
In fact, some recent studies show that even those who did not have kidney failure may develop kidney symptoms. The 2020 survey published in Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN) linked a diet high in protein with an increased risk of de novo (new onset) chronic kidney disease (CKD).


Another way that too much protein affects kidney function is that it can cause you to urinate more often. When your body enters ketosis, a metabolic state characterized by high levels of ketone bodies in the blood or urine, this can lead to dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. If this happens, you may need to increase your water intake.


Your heart health can also suffer when you eat more protein than you need, some research suggests.
“A high-protein diet, especially one high in red and processed meat, can increase the risk of heart disease because of high fat and cholesterol,” says Dasgupta.
In fact, a 2024 study published in Nature Metabolism found that consuming more than 22 percent of your daily calories from protein may increase your risk of developing atherosclerosis. This is when the blood vessels thicken or harden due to the accumulation of plaque in the inner lining of the blood vessels.
RELATED: 5 Side Effects of Taking Too Much Magnesium


Lean protein sources are an important part of a balanced diet, but getting too much protein can lead to malnutrition or imbalance.
“Protein is very filling and by focusing on protein alone, it can crowd out other nutrient-dense foods like carbohydrates and fats,” explains Mohr. “This can ultimately lead to the risk of not getting enough of other nutrients such as fiber, vitamins and minerals, which can affect overall health.”


Excess protein—especially if you eat it in place of other nutrients—can also cause gastrointestinal upset. This can take the form of nausea, diarrhea, indigestion, constipation and indigestion, experts say.


Consuming too much protein in your diet can also cause bad breath.
According to me JASN “Eating a high protein diet can lead to high levels of urea and other nitrogen products.” As the body breaks down protein during digestion, it produces ammonia if there is excess urea present, leading to an unpleasant odor.
Talk to your doctor or nutritionist to learn more about balanced nutrition, including how to get the right amount of protein for your body.
#Signs #Youre #Eating #Protein #Doctors #Health